 Violent Extremism
Violent Extremism
Extremist movements — such as ISIS, Boko Haram, the Taliban and al-Shabab — fuel, and often stem from, instability and violent conflict and present a complex challenge. The U.S. Institute of Peace works to understand the underlying causes of violent extremism and helps develop localized and viable solutions by providing research, training and expertise to practitioners and policymakers. From examining the critical role of women in combating violent extremism in Afghanistan to exploring the dynamics of radicalization in Kosovo, USIP seeks to reduce this ever-shifting threat.
Learn more in our fact sheet on USIP’s Work on Violent Extremism.
Featured Publications

Amid Central Asia’s Struggle with Extremism, Uzbekistan Promotes Pluralism
An Islamic State affiliate’s recent terror attacks in Russia, Iran and Afghanistan rang alarm bells in Central Asian capitals. Almost all the perpetrators of ISIS-Khorasan’s (ISIS-K) attacks were citizens of Central Asia, rekindling considerable concern over the threat of homegrown violent extremism in the region.

Ugandans Wield Faith and Youth Against Climate-Fueled Violence
At age five, Muhsin Kaduyu began following his father, a respected imam in southern Uganda, on missions of peace — constant meetings, mediations, consolations and prayers among Muslims and Christians in their town and surrounding farmlands. So years later, Kaduyu felt sickened when Islamist suicide bombers killed 74 soccer fans in a crowd near his university, deforming and defaming his faith. That bombing, and an anti-Muslim backlash, ignited a life’s mission that has made Kaduyu a prominent peacebuilder among millions of Ugandans who struggle for survival, prosperity and peace amid communal conflicts, violent extremism and growing climate disaster.

10 Years After ISIS’s Genocide, Iraq Is Still Dealing with the Human Legacies
This year marks the 10-year anniversary of ISIS’ capture of a third of Iraqi and Syrian territory and genocide against the Ezidis (Yazidis) and other communities. Supported by the U.S.-led Global Coalition to Defeat ISIS, Iraq declared military victory over the terrorist group in December 2017 and has significantly reduced and controlled the threat ever since. Significant progress has also been made in the recovery and stabilization process, with the successful return to their areas of origin of some five million of the six million Iraqis internally displaced by the conflict and the rebuilding of many of the regions that the conflict devastated.
Current Projects

Border Security Training Program
USIP’s Border Security Training Program trains police officers from Kenya’s Border Police Unit and General Service Unit who serve along the Kenya-Somalia border. The program increases the capacity of Kenyan police to manage conflicts nonviolently and to effectively partner with communities along the Kenya-Somalia border in order to more effectively interdict terrorist suspects and reduce justice-related drivers of violent extremism in Northeast Kenya.

Senior Study Group on Counterterrorism in Afghanistan and Pakistan
In 2022, the U.S. Institute of Peace convened a senior study group to examine the evolving threat landscape and counterterrorism challenges in South Asia. The bipartisan study group brought together experts of counterterrorism strategy, diplomacy, intelligence and South Asia to assess terrorism risks from Afghanistan and Pakistan and put forth policy options for future counterterrorism efforts in the region.
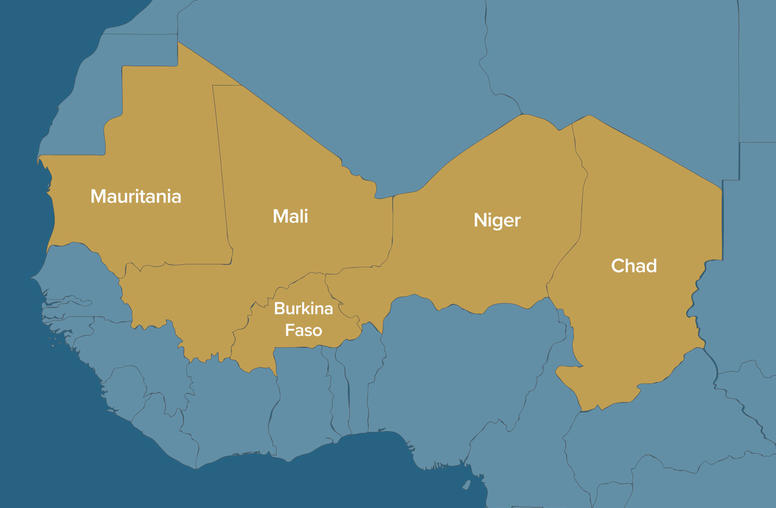
Bipartisan Senior Study Group for the Sahel
In May 2021, USIP created the Bipartisan Senior Study Group for the Sahel comprised of 12 current and former high-level U.S. officials, renowned academics and prominent Africa experts. The senior study group aims to generate new insights into the complex challenges facing the Sahel region, including food security, human rights, security assistance, private sector development and job creation — as well as great power competition. The senior study group will provide original recommendations to the U.S. government and governments in the Sahel region to improve foreign assistance, resolve conflict and support lasting peace.