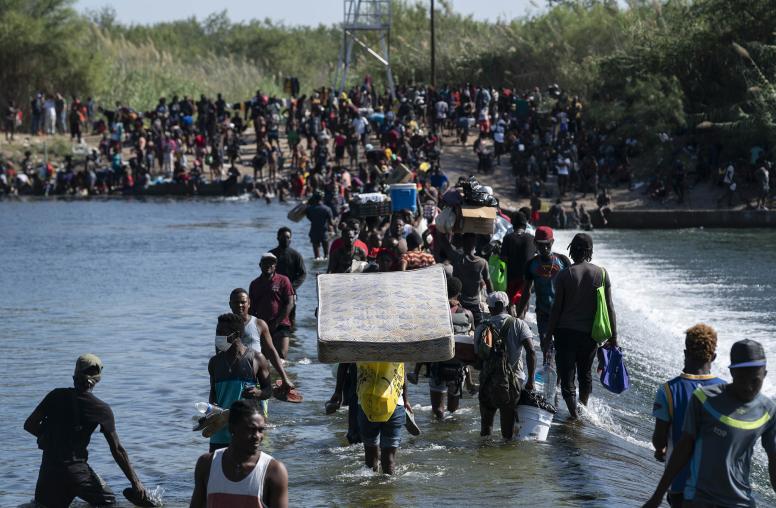
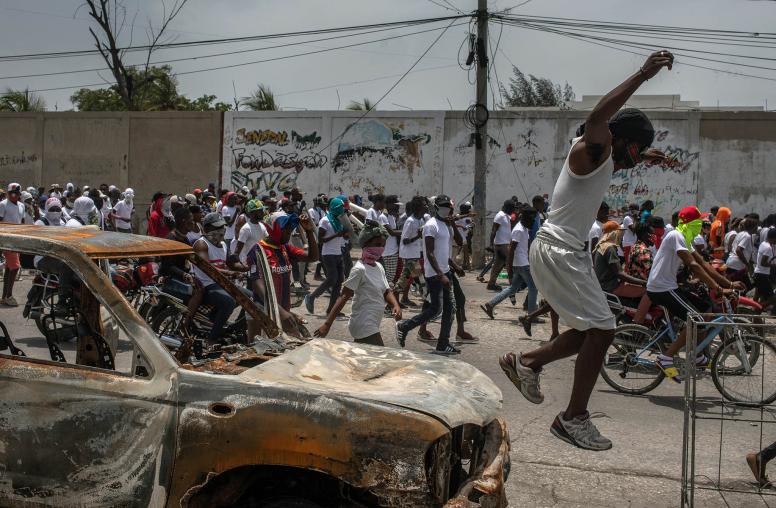While governance and economic issues have long plagued the country, Haiti’s instability has only accelerated since the assassination of President Jovenel Moïse in July 2021. Today, Haiti is experiencing a full-scale humanitarian crisis, with nearly half the population not having enough to eat. The U.N. has called for rapid action, and the United States has included Haiti in its list of priority countries under the Global Fragility Act. USIP’s Andrew Cheatham spoke with several Haiti experts about the structural and security challenges Haiti faces and possible solutions going forward.
Georges Fauriol, a senior associate at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, offers a “diagnosis” of the root causes behind Haiti’s ongoing instability crisis — as well as what the preconditions for an inclusive political process, how to balance humanitarian aid and long-term development, and the role of international actors both as part of the problem and part of the solution.
Governance and policy specialist Jeffsky Poincy looks at how corruption exacerbates Haiti’s social, political and economic issues, the role of Haiti’s active civil society — particularly youth — in facilitating a collective path forward, and the need to bolster the country’s national police and judiciary system.
Mark Schneider, a senior advisor at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, describes how fragility manifests in Haiti — from the ineffective reconstruction efforts after the 2010 earthquake to the rising dominance of gangs — as well as how a Haitian national dialogue could be orchestrated.
Vanda Felbab-Brown, director of the Brookings Institution’s Initiative on Nonstate Armed Actors, examines how Haitian gangs and armed groups managed to capture so much power, whether and how to negotiate with these violent factions, and establishing realistic goals for reducing violence and improving security.
The views and opinions expressed in these videos are those of the interviewed experts and do not necessarily reflect the views or positions of the U.S. Institute of Peace.