Understanding China’s Response to the Rakhine Crisis
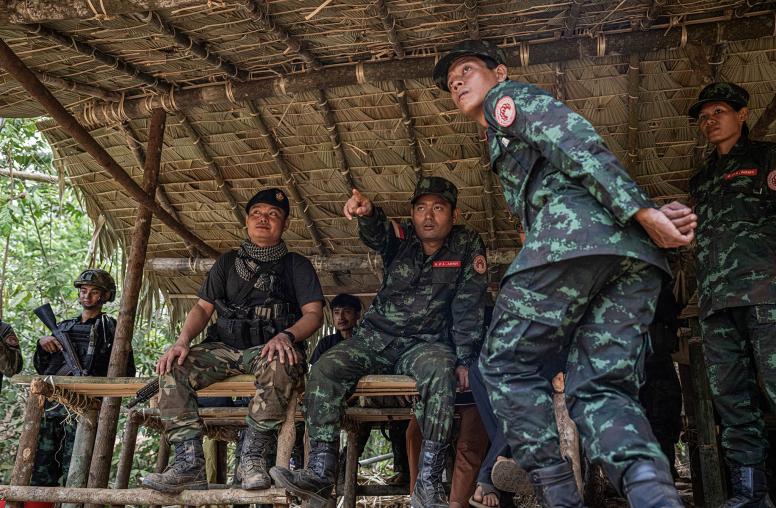
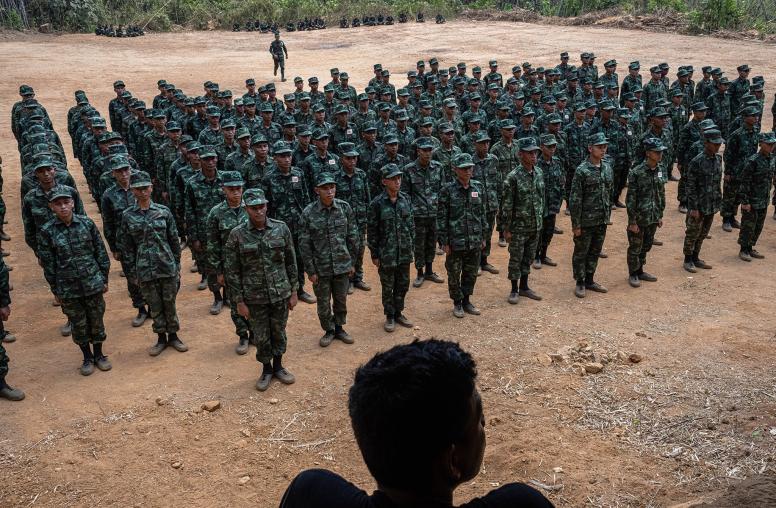
Following attacks on police posts by an armed Rohingya militia in August 2017, reprisals by the Burmese government have precipitated a humanitarian crisis. More than six hundred thousand Rohingya have fled to Bangladesh, where they face an uncertain future. Publicly stating that the root cause of conflict in Rakhine is economic underdevelopment, China—Burma’s largest neighbor and closest trading partner—has put itself in a position to promote its large-scale infrastructure investments as a means of conflict resolution. This Special Report examines the reason why Chinese engagement is likely to continue to prioritize a narrow range of issues in Rakhine that reinforce its own economic and diplomatic interests, but fail to influence the complex drivers of the current humanitarian crisis or the Burmese government’s involvement in human rights abuses.
Summary
- A major humanitarian crisis has unfolded in Burma’s Rakhine State since August 2017, after attacks by a Rohingya armed group on police posts were followed by retaliatory attacks against the Rohingya population.
- More than six hundred thousand Rohingya have fled to Bangladesh, and reports of human rights abuses have sparked widespread international condemnation, particularly from Western nations and Organization of the Islamic Conference (OIC) countries.
- In contrast, China’s response has been largely supportive of the Burmese government—in effect affirming Burma’s characterization of the attacks as “terrorism.” Military cooperation between the two states has also been reaffirmed.
- Publicly stating that the root cause of conflict in Rakhine is economic underdevelopment, China has promoted its large-scale infrastructure investments in the state (including a deep-sea port, and oil and gas pipelines) as a means of conflict resolution.
- Going forward, Chinese engagement in the conflict is likely to continue to address a narrow range of issues that reinforce its own interests and narrative, but do not influence the complex drivers of the current humanitarian crisis or the Burmese government’s involvement in human rights abuses, which others in the international community are calling to investigate.
About the Report
Following attacks on police posts by a Rohingya militia in August 2017, Burmese military attacks on the predominantly Muslim Rohingya population in Rakhine State have forced more than six hundred thousand Rohingya to flee to Bangladesh. Supported by the Asia Center at the United States Institute of Peace, this report examines China’s interests and influence in Rakhine State and its continuing support of the Burmese government and military during the ongoing humanitarian crisis.
About the Author
Adrienne Joy is a Yangon-based independent consultant, specializing on the Burma’s peace process and China-Burma relations. Her work has included extensive analysis on the dynamics between ethnic armed groups, the government, and the Tatmadaw.