Europe’s Refugee Crisis Shows Ukraine’s Resilience
Ukraine Has Absorbed 1.5 Million Displaced; Soon It Must Employ Them
With Europe awash in more than a half-million refugees from Middle Eastern and other wars, it might be easy to overlook Ukraine’s response to its own population—nearly three times the size, at 1.5 million—displaced by the Russian-backed war in the east.

More than 18 months into the crisis, Ukraine has absorbed its uprooted citizens with no significant social unrest—a tribute to the resilience of both the displaced people and the communities hosting them. Ukraine’s challenge now is to provide economic opportunity and growth that can help meet the needs of both the displaced and their hosts.
“More than 18 months into the crisis, Ukraine has absorbed its uprooted citizens with no significant social unrest or communal violence.”
As former Swedish Prime Minister Carl Bildt noted in a Twitter message last month, the international community “must certainly not ignore the refugee and displacement crisis in Ukraine.” Yet UNHCR said this month it has received just 56 percent of the $41.5 million it sought from donors this year to fund its work on the Ukraine crisis. The agency had to suspend its work last month in the part of Luhansk oblast controlled by Russian-backed separatist militias after the Luhansk authorities expelled international aid groups.
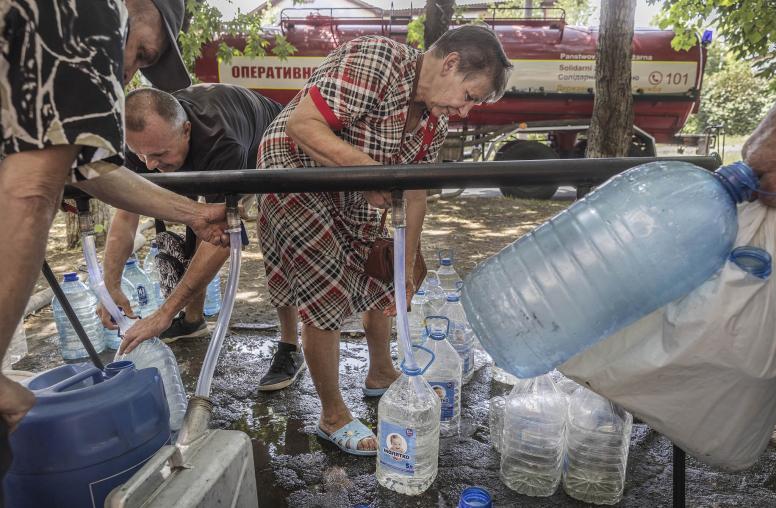
While Ukraine’s refugee crisis is massive, the country has no tent cities to dramatize it for TV cameras. Instead, refugees are being absorbed into cities and towns. The eastern oblast (province) of Dnipropetrovsk has taken in more than 73,000 people, most of whom fled the fighting in neighboring Donetsk. Yet the atmosphere of Dnipropetrovsk city was one of outward normalcy when I visited last July.
We must certainly not ignore the refugee and displacement crisis in Ukraine. Help needed.http://t.co/bK0dcclGW3
— Carl Bildt (@carlbildt) September 9, 2015
With the central government overstretched in dealing with the existential threats of Russian aggression and economic crisis, the influx of the displaced did not get the focused attention from the leadership in Kyiv it otherwise might have when it began in 2014. Fortunately, Ukraine’s vibrant civil society rose to the challenge. Ukrainian non-government organizations—most staffed by volunteers—sprang into action to offer housing, food, legal advice and psychological counseling. Volunteers used social media to pass information and raise funds.
The eastern city of Kharkiv has been a hub for refugees from the war in the Donbas region to the south. (Relief organizations refer to them formally as “internally displaced persons,” or IDPs, because they have not crossed an international border.) Hromadske TV, which emerged out of the Maidan movement, provided a sense of the often heroic work of volunteers helping IDPs in Kharkiv. And it broadcast a half-hour, English-language documentary on the conditions nationwide for displaced people facing resettlement, including the traumas that they, particularly children, have suffered.
Local governments also stepped in. At the Kirovograd oblast administration headquarters in central Ukraine a year ago, officials were eager to show me their offices for registering and helping the displaced. The officials said housing had been found for several thousand people, with modest subsidies provided to those in need. Most arrivals are housed in privately rented apartments or vacant dachas. Conditions are often crowded but far more comfortable and less isolating than camps would be.
International relief agencies are helping. The U.N. refugee agency, UNHCR, has field offices in several oblasts adjacent to the conflict zone. When I visited its office in Dnipropetrovsk last July, representatives stressed the need for economic development in the areas of settlement. Given the destruction inflicted on Donbas, it is likely that many IDPs will be staying for years, if not permanently, in their place of relocation. The task thus now shifts to finding jobs for those able to work so they can provide for themselves.
Promote Dialogue with the Displaced
Friction between refugees and their host communities may increase as the displacement is prolonged. Most IDPs have chosen to settle in oblasts near the conflict zone. While all of Ukraine is in steep recession, the eastern oblasts have been hardest hit. Resentment against IDPs may rise if they are seen to be soaking up scarce resources or competing for the few available jobs.
Women are disproportionately represented among the displaced and risk violence as partners become dejected or alcoholic at having few or no prospects. Pensioners are a majority of registered IDPs in many regions and face particular difficulties navigating the bureaucracy to secure pensions and travel permits.
Fostering dialogue between IDPs and their host communities is crucial to mitigating tensions in the months and years ahead. Displaced people will need to find their own voice through IDP organizations and insist that their needs be addressed as part of any peace process.
Securing voting rights also is vital. With Ukraine preparing for local elections on October 25, Ukraine’s parliament considered several bills that would have set procedures for IDPs to vote in their places of settlement. But those measures remain pending and the displaced will be unable to vote this time.
The displacement crisis, while traumatic, has also revealed the impressive resilience of the Ukrainian people. The responsiveness of civil society prevented what could have been a tragedy. Receiving communities, despite their own privations, rose to the challenge. However, humanitarian aid will not address the longer-term problem of unemployment among IDPs. With the fighting in Donbas having at least temporarily subsided, national reforms to reduce corruption, improve the investment climate and spur employment – in the east and throughout Ukraine – would do more than anything to ease the plight of Ukraine’s uprooted 1.5 million.
Colin Cleary is a Foreign Service officer and fellow at USIP who served as political counselor at the U.S. Embassy in Kyiv in 2008-2012. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily represent those of the State Department or the U.S. government.