Publications
Articles, publications, books, tools and multimedia features from the U.S. Institute of Peace provide the latest news, analysis, research findings, practitioner guides and reports, all related to the conflict zones and issues that are at the center of the Institute’s work to prevent and reduce violent conflict.
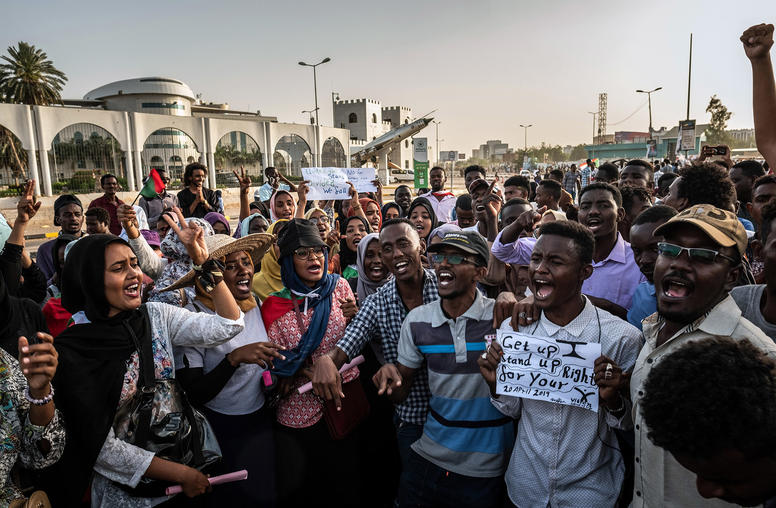
Five Key Considerations To Make the U.S. Global Fragility Strategy Work
Even as the public debate over the U.S. military withdrawal from Afghanistan continues, the State Department and USAID are quietly putting plans in place to test a new approach to con-flicts overseas. Drawing on the hard-earned lessons from Afghanistan and Iraq over the past two decades, this approach would have the United States rely far less on military power and far more on sustained — but much less costly — diplomacy and closely coordinated development investments. If fully implemented, consistent with the recently enacted Global Fragility Act, this new effort promises to help stabilize countries in their recovery from COVID-19 and the knock-on shocks to their economies.
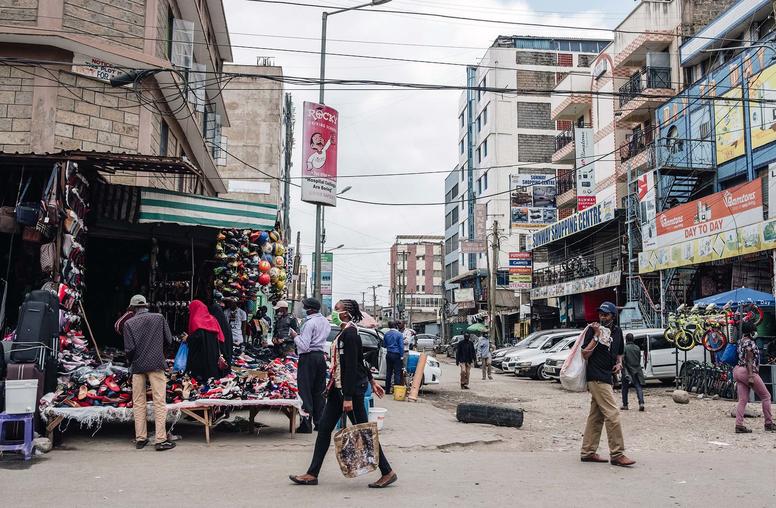

A New U.S. Approach to Help Fragile States Amid COVID-Driven Economic Crisis
The global economy is projected to rebound from the effects of COVID-19 in 2021, but the world’s most fragile states may not share in the upswing. Saddled with economic collapse and soaring debt, developing economies are likely to be left further behind after shrinking about 5 percent last year, according to World Bank estimates. As a result, over 55 million people could be plunged deeper into poverty, fueling social and political grievances and increasing the risks of instability.
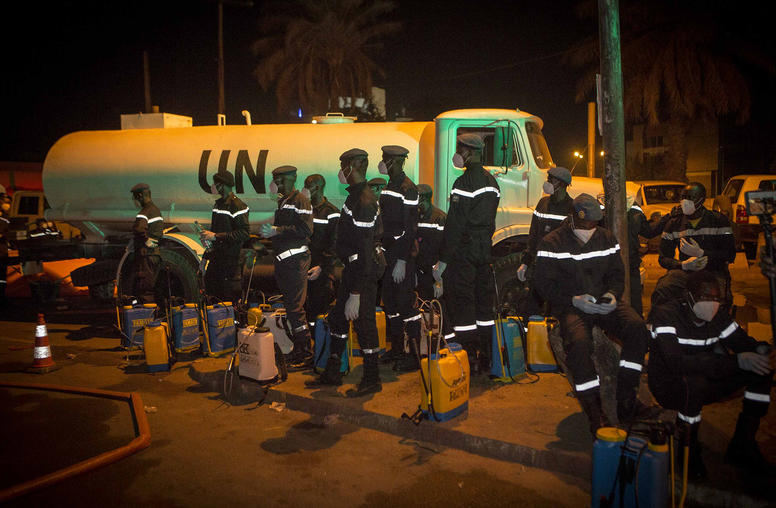
Four Lessons for Cease-fires in the Age of COVID
During his opening remarks at the 75th U.N. General Assembly, Secretary-General António Guterres renewed his appeal for a global humanitarian cease-fire, urging the international community to achieve one in the next 100 days. But in the roughly 180 days since his initial appeal, most conflict parties have not heeded the secretary-general’s plea. What can peacebuilders do to advance the secretary-general’s call? Four key lessons have emerged over the last six months on how cease-fires can be achieved—or stalled—by COVID-19.

Tyler Beckelman on the Virtual U.N. General Assembly
While this year is the U.N.’s 75th Anniversary, the General Assembly was a “more muted affair” than expected, says USIP’s Tyler Beckelman. Member states had a chance to discuss the newly signed Abraham Accord and the future of multilateral diplomacy, but virtual summitry is “no substitute for meeting in person.”
Six Things to Watch at the U.N. General Assembly
This year’s United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) meeting, happening against the backdrop of the 75th anniversary of the U.N.’s founding, was supposed to be a major milestone—a moment for world leaders to reflect on the organization’s pursuit of peaceful international cooperation since the devastation of World War II, and to consider how the multilateral system should evolve to tackle the 21st century’s biggest challenges. Instead, the COVID-19 pandemic has upended the traditional in-person gathering at the U.N.’s headquarters in New York City. This UNGA will be a much more muted affair, with participants using the same videoconferencing technology to which we have all become accustomed in 2020. But the challenges facing the international system are as pressing and complicated as ever. As UNGA goes virtual, here are six issues to watch.
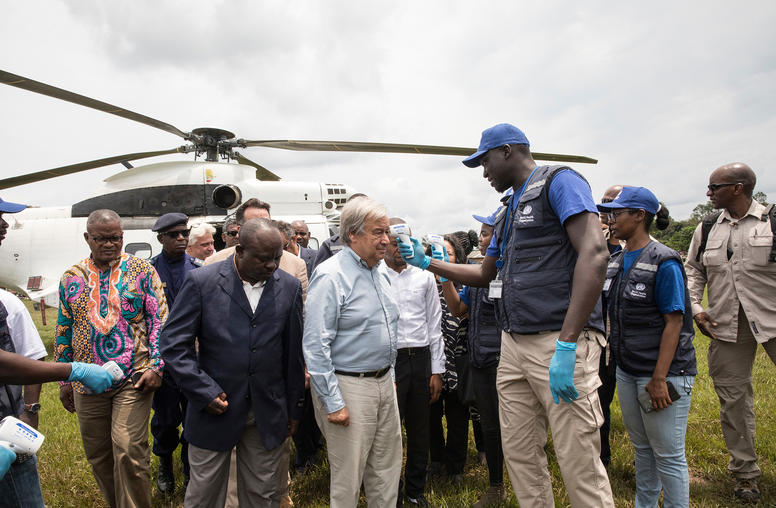

Amid COVID, We Need Enhanced International Coordination to Build Peace
As the humanitarian and economic toll of the COVID-19 pandemic continues to grow, so does the risk that this crisis will fuel new conflicts around the world, while stymying prospects for resolving ongoing ones. The global health crisis is triggering devastating levels of food insecurity and unemployment, especially in the world’s most fragile states, where the social contract between citizens and the state is severed and societies are fragmented and vulnerable to violence. These trends will almost certainly lead to a future spike in instability across these countries, unless concerted international action is taken.
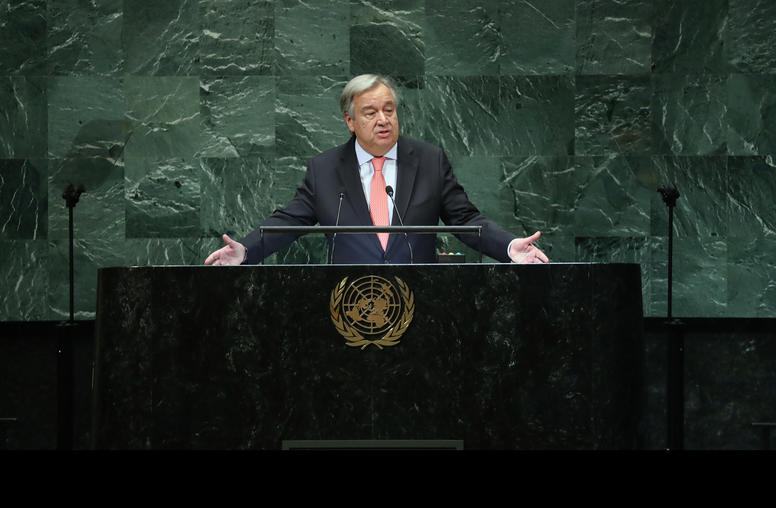

U.N. Finally Endorses a COVID Cease-fire: Will it Make a Difference?
After months of negotiation and diplomatic wrangling, the U.N. Security Council (UNSC) on July 1 unanimously adopted resolution 2532, endorsing U.N. Secretary-General Guterres’ late March call for a global cease-fire. Diplomats in New York hailed the resolution as an overdue win for multilateralism, while Pope Francis called for the resolution to be implemented “effectively and promptly.” Coming months after the secretary-general’s original cease-fire call and the global spread of the pandemic, will the resolution help bring peace?

Is the International Community Missing an Opportunity To Advance Peace?
On March 23, U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres appealed for a global cease-fire to combat the COVID-19 pandemic. Yet over eight weeks later, the Security Council has not been able to muster consensus on a resolution to support even a humanitarian, time-limited cease-fire, despite early and repeated warnings about the potential devastation that the virus will bring to conflict zones.

Tyler Beckelman on Cooperation to Combat Coronavirus
A “mixed” response from the international community is threatening a worst-case scenario for fragile states facing COVID-19. USIP’s Tyler Beckelman says countries need to recognize “the best strategy for defeating the virus is defeating it everywhere” and cooperate on aid in fragile contexts.
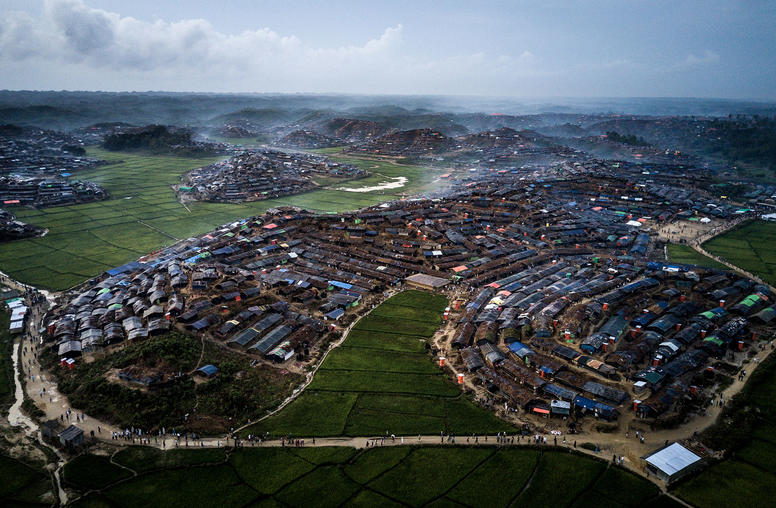

The Coronavirus Requires Global Cooperation—Now
As the world’s privileged cope with the COVID pandemic through telework and sheltering at home, millions of people face grim struggles for survival, packed into informal settlements or camps for people already displaced in war-torn or fragile states. Governments have missed opportunities for a stronger international response, partly because of great-power rivalries. The economically powerful Group of 20 nations and international financial institutions have made a start at buoying the world’s economy—but other multilateral forums are mired in stasis. The U.N. Security Council should act to get ahead of the pandemic in fragile states and seize the moment to advance peace in some of the world’s most intractable conflicts.