Research & Analysis
U.S. Institute of Peace’s articles, reports, tools and other features provide policy analysis, research findings, and practitioner guides. These publications examine critical conflict issues at the center of the Institute’s work to prevent and resolve violent conflict.
The views expressed in these publications are those of the author(s).
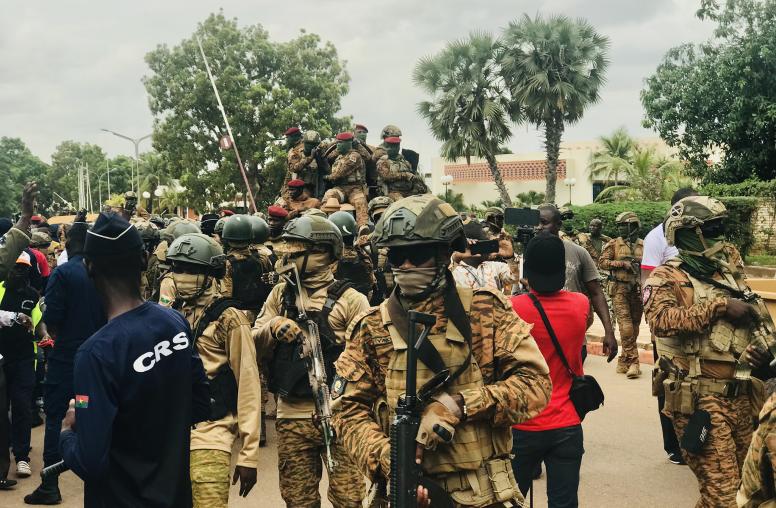

In Africa, the Need to Engage with Democracies and Coup Regimes
Three West African coup leaders — a general, a colonel and a captain — gathered last weekend to formally ally their regimes in Niger, Mali and Burkina Faso. Their meeting dramatized two realities for Americans and allies who hope to see our children live in a world governed by laws rather than brute force.

Joseph Sany on the U.S. Withdrawal from Niger
The U.S. reached an agreement with Niger’s military junta to close two military bases in the country in what amounts to a “tactical setback” for counterterrorism efforts in the Sahel. But the closure also “forces the U.S. to review its military posture in the region,” says USIP’s Joseph Sany, adding “there may be other options.”
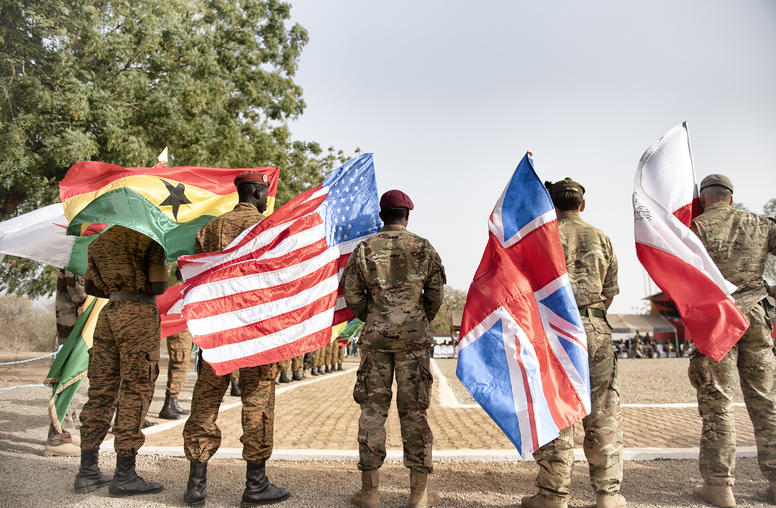

For Sahel Stability, U.S. Needs Broader, Coordinated Policy
As military coups and violent insurgencies have spread across Africa’s Sahel over the past decade, U.S. policy has professed to recognize and address their interconnections across the region, notably through the Trans-Sahara Counterterrorism Partnership. Yet this effort remains insufficient to meet the scale and complexity of the violence and the underlying failures of governance.
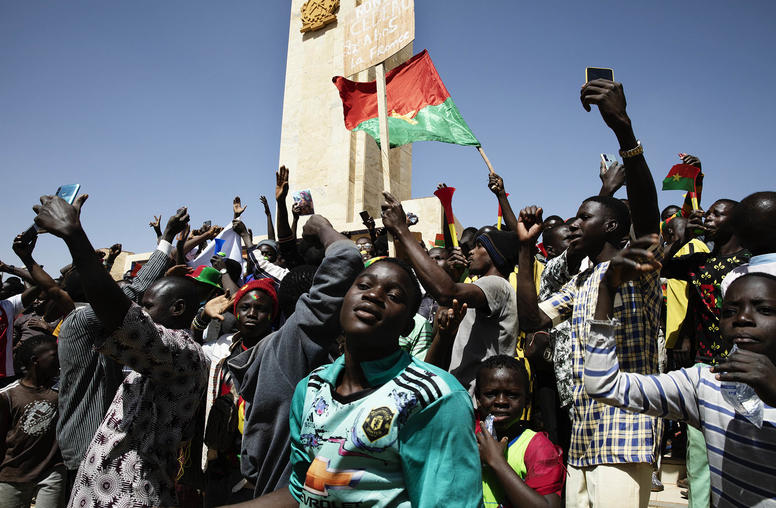
For Peace in Sahel, African and U.S. Experts Urge Focused Partnership
The past month has sharpened a decade-old question for U.S. and international policymakers: How best, in 2024, to help stabilize what is now the world’s largest single zone of military rule and violent conflicts — Africa’s Sahel region? After three military-ruled Sahel states withdrew from the West African regional community in January, those juntas last week proclaimed an alliance aimed at resisting international pressures, including those for their return to elected civilian rule. Former U.S. and African officials yesterday urged what they called vital changes in U.S. and allied policies to prevent a dangerous spread of the Sahel’s crises.
Senior Study Group for the Sahel: Final Report and Recommendations
The United States has not traditionally viewed the Sahel as a region of vital interest, whether in terms of security or from an economic or business perspective. This has led to a pattern of reactive involvement shaped by the circumstances of specific events rather than proactive commitments. This pattern reveals the lack of a comprehensive strategy for the volatile Western Sahel region, which includes Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, and Niger. In April 2022, President Joe Biden announced that the US government would advance the “U.S. Strategy to Prevent Conflict and Promote Stability” in coastal West Africa by prioritizing a partnership with Benin, Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, and Togo.

For Peace in the Sahel, Can the U.S. Work with Algeria?
Amid the Sahel region’s crises — a continent-spanning web of communal and terrorist insurgencies and eight coups d’etat since 2020 — U.S. and European attention is focused elsewhere: on Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, China’s expanding global influence and the Israel-Palestine conflict. But an opportunity to promote stabilization in the Sahel, notably in Mali and Niger, could be U.S. collaboration with Algeria. Algeria shares borders with those violence-stricken states, and also the U.S. desire to help stabilize them and their Sahel neighbors. A first question for any joint U.S-Algerian engagement is whether the two countries’ visions for Sahel stability, particularly in Mali and Niger, are aligned or contradictory.

Can Algeria Help Niger Recover From Its Army Coup?
Democracies and democracy advocates should welcome this week’s tenuously hopeful sign in Algeria’s announcement that the 10-week-old military junta in Niger has accepted Algiers’ offer to mediate in a transition to civilian, constitutional rule. Still, Algeria’s government and the junta left unclear the extent of any agreement on mediation, notably disagreeing on a basic element: the duration of a transition process. Algeria can bring significant strengths to a mediating role. In stepping forward from what most often has been a cautious posture in the region, Algeria creates an opportunity that international partners should seek to strengthen.

How to Respond to Niger’s Coup — and Prevent the Next One
Military officers in Niger are rushing to consolidate the power they seized 15 days ago, while West Africa’s elected governments and regional institutions are seeking ways to reverse the July 27 coup d’état. Niger’s coup seems a particular setback for democracy, completing a six-nation belt of military regimes across Africa’s Sahel region. Amid this uncertain power struggle, how can the world support Africans’ demonstrated demand for elected, democratic governance that meets their peoples’ needs? We should begin by hewing to several basic principles. One is to keep our responses to coups coherent — but not uniform. Niger’s coup is distinct; our response must be as well.

West Africa’s Leaders Face the High Stakes of Niger’s Coup
Amid the global challenges to building international stability and peace, a crisis increasingly forcing itself to the foreground — even amid those of record human displacement, climate degradation and unresolved wars — is the plunge by six countries across Africa’s Sahel region into coups d’état and military rule. Eight coups since 2020 have left 150 million people under rule by their armed forces. The latest coup, in Niger, is drawing a heightened international response, and a key player, the 15-nation West African community, today that it will pursue a long campaign of economic and diplomatic pressure, and that it sees military force as a last resort.

Countering Coups: How to Reverse Military Rule Across the Sahel
Three years of coups around Africa’s Sahel region — eight of them in six nations, from Guinea on the Atlantic to Sudan on the Red Sea — leave many African and other policymakers frustrated over how to respond. The Sahel’s crises have uprooted more than 4 million people and could add millions more to our record levels of global human migration as Africa’s population grows and its climate destabilizes. Yet the pattern of coups and other evidence — notably from USIP’s Sahel fieldwork, counter-coup research and bipartisan analysis teams — offer guidelines for effective responses by African, U.S. and international policymakers.