Justice and Security Needs in Iraq after ISIL
Understanding Displaced Populations’ Concerns with Returning Home
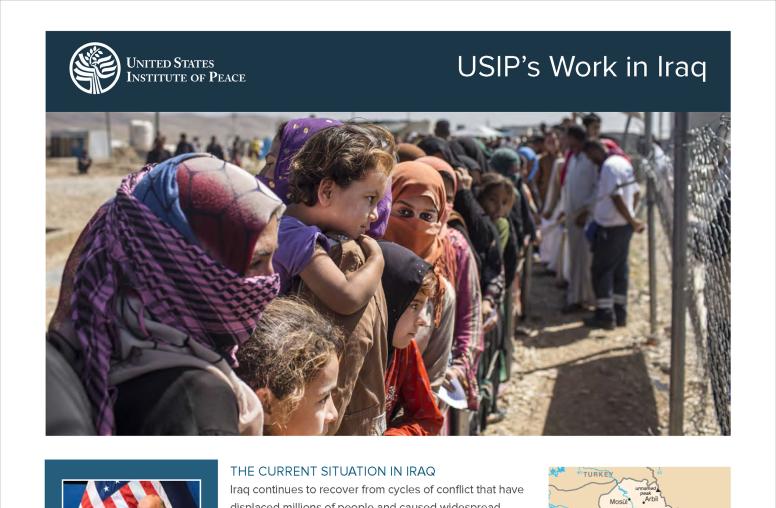
Many of the three million-plus internally displaced persons (IDPs) living in Iraq wish to return to their homes in areas no longer controlled by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL). But weak security and informal justice in these areas make safe return a challenge. IDPs, civil society organizations, and official stakeholders met in Baghdad, Karbala, and Kirkuk under USIP’s Justice and Security Dialogue program to voice concerns about and offer suggestions for safe return. This Special Report summarizes these discussions, which could guide policymakers seeking to resolve the IDP crisis and sustain security in Iraq.
Summary
- Liberating areas from the control of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) will not fully resolve the internally displaced person (IDP) crisis in Iraq. IDPs’ concerns must be addressed in a comprehensive and credible plan that facilitates safe, voluntary return to liberated areas.
- IDPs’ concerns about return highlight the conditions that contributed to ISIL’s rise in the first place, such as lack of governance, destroyed infrastructure, overlapping security authorities, and an inefficient judiciary system. Preexisting societal cleavages have been aggravated and augmented in recent years. Safe and sustainable return probably will not happen unless broader issues of security, justice, and reconstruction are addressed.
- Along with organizing and securing IDPs’ journey back to their homes, security forces must be able to maintain stable provincial and national borders and turn back ISIL counterattacks.
- Police forces will have to be rebuilt and reformed to establish trust with local populations and to prevent conflicts between IDPs and those who supported ISIL or remained in place after ISIL took control.
- Fair and effective courts and other justice sector actors are required to prevent mass revenge and informal justice proceedings.
- To make IDPs’ return viable and to prevent actors from further embracing extremism, the government of Iraq (GOI) must not only provide support for IDPs’ return to areas they left, but also reconstruct these areas and promote employment opportunities in them as a means of enabling and sustaining local stability.
About the Report
As part of a four-year iterative United States Institute of Peace (USIP) program that promotes community-level collaborative approaches to justice and security issues, the Justice and Security Dialogue team, in partnership with the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor and the Bureau of International Narcotics and Law Enforcement Affairs, engaged internally displaced persons (IDPs) and relevant stakeholders in Baghdad, Karbala, and Kirkuk to address IDPs’ return to newly liberated areas. This Special Report summarizes the concerns expressed and recommendations made by Iraqi IDPs, civil society organizations, and official government stakeholders during these dialogue sessions. It highlights the complexity involved in returning IDPs to areas liberated from the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL). It also offers a window into the deep apprehension IDPs feel about the prospect of return. Finally, it makes recommendations for sustaining security and stability and for promoting formal justice. The concerns and recommendations documented here provide a map of the social and political landscape surrounding safe return of IDPs, one that policymakers can use in developing more holistic approaches to resolving the IDP crisis and sustaining security in Iraq.
About the Author
Khitam Alkhaykanee is an Iraqi from Baghdad who has worked for USIP since 2004. She manages USIP’s Justice and Security Dialogue programs in Libya and Iraq. Her work involves establishing trust between justice and security actors and communities as well as developing relationships that promote collaboration and problem solving. Her interests include peacebuilding through community policing and developing inclusive conflict-resolution processes that engage vulnerable groups, especially women and youth.