Publications
Articles, publications, books, tools and multimedia features from the U.S. Institute of Peace provide the latest news, analysis, research findings, practitioner guides and reports, all related to the conflict zones and issues that are at the center of the Institute’s work to prevent and reduce violent conflict.
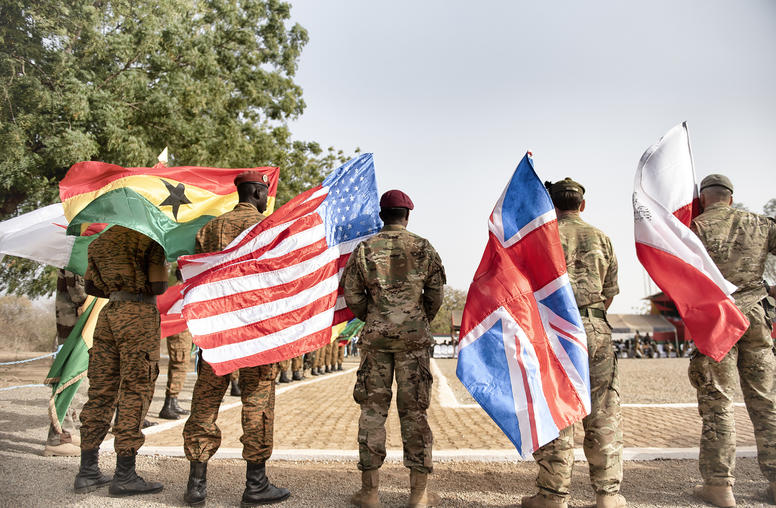

For Sahel Stability, U.S. Needs Broader, Coordinated Policy
As military coups and violent insurgencies have spread across Africa’s Sahel over the past decade, U.S. policy has professed to recognize and address their interconnections across the region, notably through the Trans-Sahara Counterterrorism Partnership. Yet this effort remains insufficient to meet the scale and complexity of the violence and the underlying failures of governance.
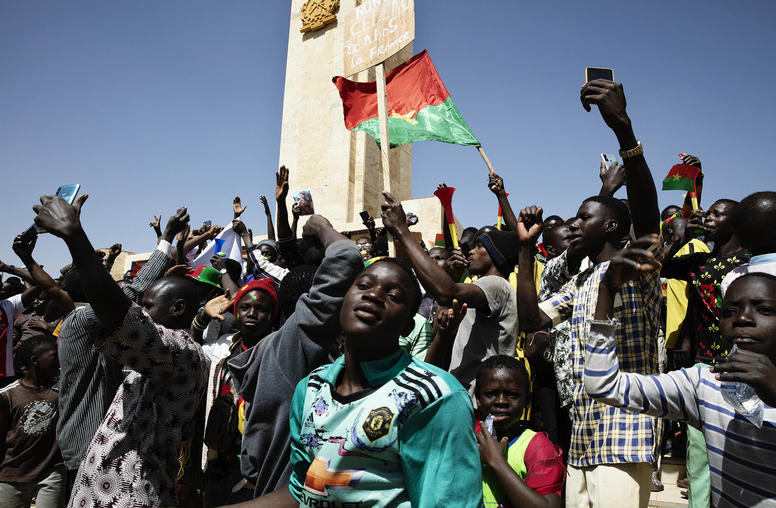
For Peace in Sahel, African and U.S. Experts Urge Focused Partnership
The past month has sharpened a decade-old question for U.S. and international policymakers: How best, in 2024, to help stabilize what is now the world’s largest single zone of military rule and violent conflicts — Africa’s Sahel region? After three military-ruled Sahel states withdrew from the West African regional community in January, those juntas last week proclaimed an alliance aimed at resisting international pressures, including those for their return to elected civilian rule. Former U.S. and African officials yesterday urged what they called vital changes in U.S. and allied policies to prevent a dangerous spread of the Sahel’s crises.
Senior Study Group for the Sahel: Final Report and Recommendations
The United States has not traditionally viewed the Sahel as a region of vital interest, whether in terms of security or from an economic or business perspective. This has led to a pattern of reactive involvement shaped by the circumstances of specific events rather than proactive commitments. This pattern reveals the lack of a comprehensive strategy for the volatile Western Sahel region, which includes Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania, and Niger. In April 2022, President Joe Biden announced that the US government would advance the “U.S. Strategy to Prevent Conflict and Promote Stability” in coastal West Africa by prioritizing a partnership with Benin, Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, and Togo.

For Peace in the Sahel, Can the U.S. Work with Algeria?
Amid the Sahel region’s crises — a continent-spanning web of communal and terrorist insurgencies and eight coups d’etat since 2020 — U.S. and European attention is focused elsewhere: on Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, China’s expanding global influence and the Israel-Palestine conflict. But an opportunity to promote stabilization in the Sahel, notably in Mali and Niger, could be U.S. collaboration with Algeria. Algeria shares borders with those violence-stricken states, and also the U.S. desire to help stabilize them and their Sahel neighbors. A first question for any joint U.S-Algerian engagement is whether the two countries’ visions for Sahel stability, particularly in Mali and Niger, are aligned or contradictory.
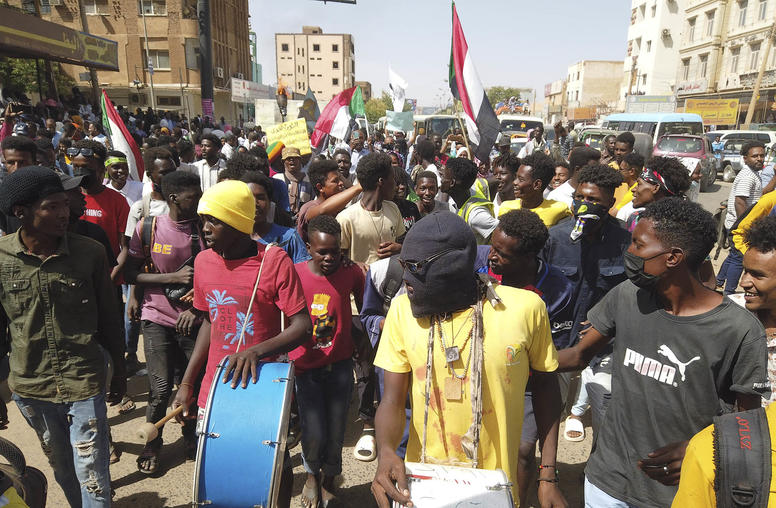

Countering Coups: How to Reverse Military Rule Across the Sahel
Three years of coups around Africa’s Sahel region — eight of them in six nations, from Guinea on the Atlantic to Sudan on the Red Sea — leave many African and other policymakers frustrated over how to respond. The Sahel’s crises have uprooted more than 4 million people and could add millions more to our record levels of global human migration as Africa’s population grows and its climate destabilizes. Yet the pattern of coups and other evidence — notably from USIP’s Sahel fieldwork, counter-coup research and bipartisan analysis teams — offer guidelines for effective responses by African, U.S. and international policymakers.
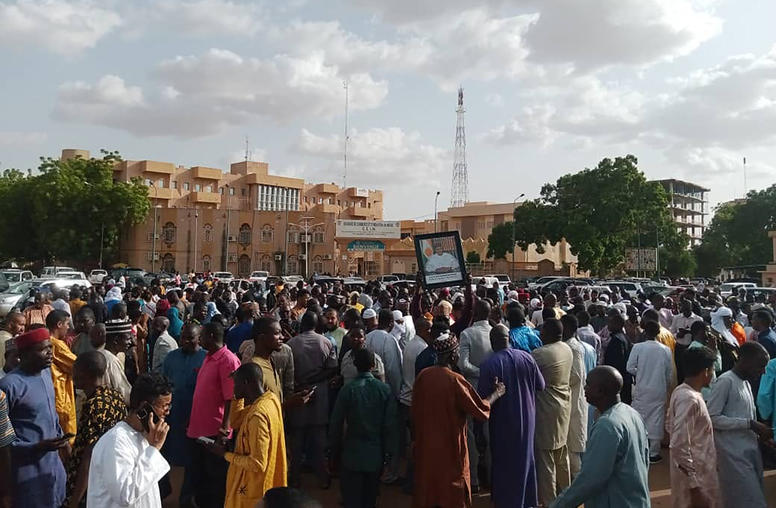
A Coup in Niger: What It Means for Africa, U.S. and Partners
This morning’s coup d’etat in Niger only deepens the pattern of instability across Africa’s Sahel and damages what has been a rare process of fairly steady democracy building in the region. Niger’s democratically elected government has been a valued partner for African and international efforts to stabilize the Sahel against its web of insurgencies, extremist movements and military coups. Kamissa Camara, a former foreign minister of Niger’s neighbor, Mali, now an analyst on the region with USIP, says the coup underlines lessons already evident about how to improve international efforts to build democracy and peace.
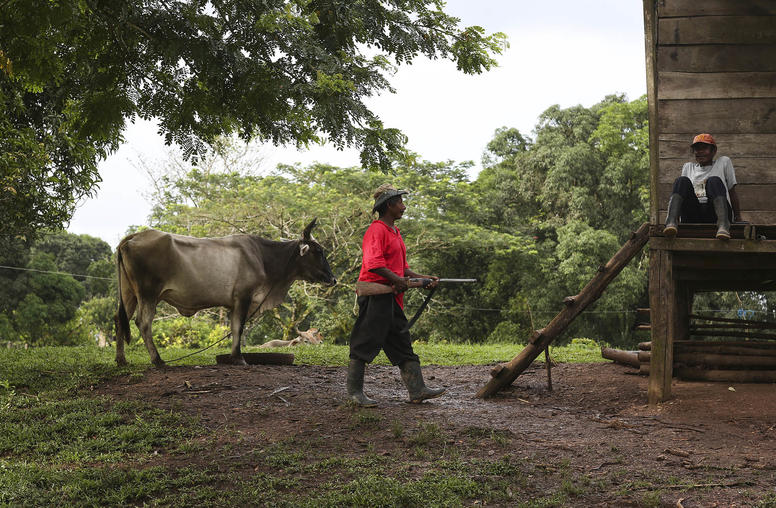

Earth’s best defenders are Indigenous. They pay a price: violence.
Little noted by the world, warfare in India’s northeastern state of Manipur this spring has killed hundreds of Indigenous people and uprooted more than 35,000 residents. This violence along the India-Myanmar border fits a global pattern, also little noted: For decades, some 80 percent of human conflicts have smoldered in the “biodiversity hotspots” where our planet’s flora and fauna are most threatened by battles for resources and wealth — and where Indigenous peoples suffer the violence while protecting humanity’s common ecological heritage. We should strengthen the world’s inadequate public attention and policies on this crisis, and 2023 offers a chance to do so.
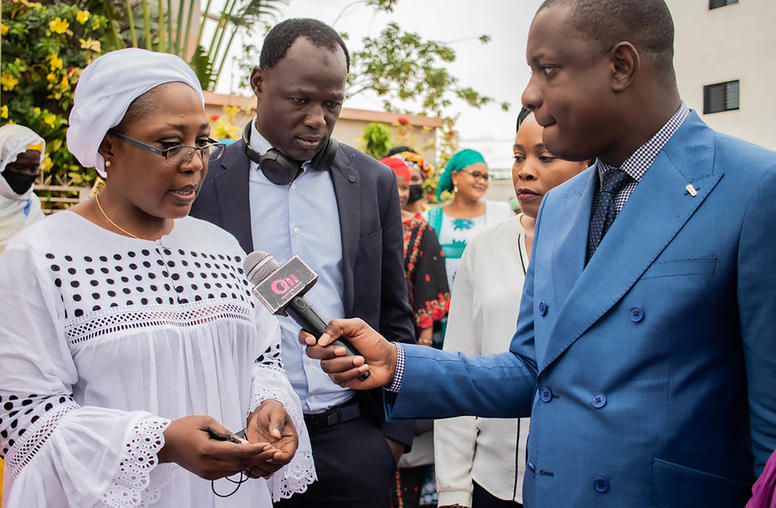

Au Mali, la société civile joue un nouveau rôle dans la transition démocratique
Au cours de la décennie qui a précédé les deux coups d'État militaires de 2020 et 2021 au Mali, les griefs persistants en matière de gouvernance ont priver les civils de services publics fiables, pendant que l'armée s’efforçait de contenir les groupes extrémistes violents. L'espoir d'un retour rapide à un régime civil après le coup d'État s'est estompé au fur et à mesure que le pays approche sa troisième année sous un régime militaire. En dépit des efforts du gouvernement de transition pour établir une feuille de route pour les élections de 2024, des préoccupations s’agrandissent par rapport à la capacité de l'infrastructure nécessaire pour mener à bien le processus et s'aligner sur le calendrier prévu.

In Mali, Civil Society Takes on New Role in the Democratic Transition
In the decade leading up to Mali’s two military coups in 2020 and 2021, persistent governance grievances had left civilians without reliable public services while the military struggled to contain violent extremist groups. Hopes for a quick return to civilian rule post-coup have faded, as the country now nears three years under the rule of military leaders. While the transitional government has laid out a roadmap toward 2024 elections, there are growing concerns about the infrastructure capacity to carry out elections within that timeframe.
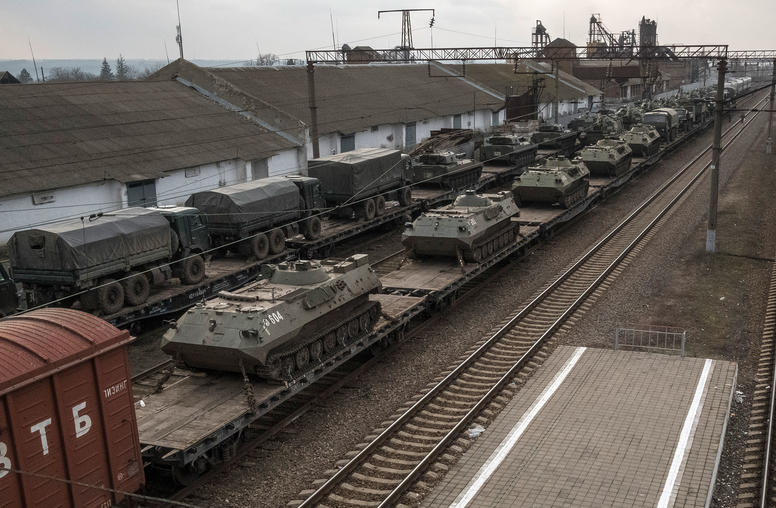

How Putin’s Invasion of Ukraine Affects the Rest of Russian Foreign Policy
USIP’s Heather Ashby, Jude Mutah, Andrew Scobell and Mona Yacoubian examine how the invasion of Ukraine might have shifted Moscow’s decision-making in other regions — such as Syria, the Sahel and China.