Déby’s Chad
Political Manipulation at Home, Military Intervention Abroad, Challenging Times Ahead
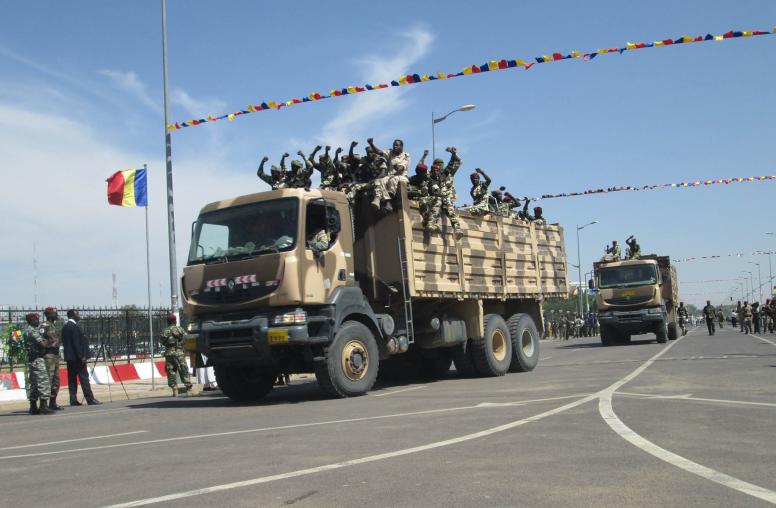
Since gaining its independence from France in 1960, Chad has evolved from a one-party state into a multiparty regime, endured successive rebellions, and become an interventionist regional actor. Thanks to both an oil boom and corruption, segments of the Chadian elite have become very rich, but most of the population is mired in poverty. This report examines the country’s political system, which has kept President Idriss Déby in power for twenty-seven years, and the country’s recent foreign policy, which is notable for a series of regional military interventions, to assess Chad’s current and future regional role.
Summary
- In recent years, thanks to its military interventionism, Chad has acquired a new regional and international status. This new role gives President Idriss Déby Itno, who took power by force in 1990, global political capital and leads international partners to turn a blind eye to his country’s weak democracy.
- Chad is still vulnerable to regional threats. Its military intervention against Boko Haram makes it a target for that extremist group, and although N’Djamena is sometimes seen as a bulwark of regional stability, its interference abroad, notably in the Central African Republic, has had a destabilizing impact.
- An oil-producing country, Chad has been hit hard by the drop in global oil prices. The severe economic problems facing Chad, however, have deeper roots. Meanwhile, austerity measures have triggered strikes and massive protests in a country where most citizens are desperately poor.
- The root causes of the various crises that have beset Chad have never been addressed. Déby has been able to retain his grip on the presidency thanks to an unpopular modification of the constitution in 2005 and subsequent rigged elections up to and including the contested 2016 vote.
- Although power remains concentrated within Déby’s ethnic group, the regime has been able to co-opt elites from other regional and ethnic backgrounds.
- The country may be plunged into crisis if arrangements are not made in advance for a Déby successor. The question of how to transfer power is made more complex because the current regime’s repressive tactics and divide-and-rule strategy have hindered the formation of a strong civilian opposition.
About the Report
This report examines Chad’s political system, which has kept President Idriss Déby in power for twenty-seven years, and recent foreign policy, which is most notable for a series of regional military interventions, to assess the impact of domestic politics on Chad’s current and future regional role—and vice versa. A joint publication of the United States Institute of Peace (USIP) and the Institute for Security Studies (ISS), the report is derived from several hundred interviews conducted in Chad, the Central African Republic, Niger, France, and other countries, between October 2015 and October 2017 as well as desk research. Unless otherwise cited, statements in this report are drawn from these interviews.
About the Authors
Jérôme Tubiana is a researcher who specializes in Chad, Sudan, and South Sudan. He has conducted numerous field research missions in conflict areas for various organizations, most notably the Small Arms Survey and the International Crisis Group. His publications include two studies on Darfur for USIP, a book on the Darfur conflict (Chroniques du Darfour, 2010), and various articles in Foreign Affairs, Foreign Policy, the London Review of Books, and Le Monde diplomatique. Marielle Debos is an associate professor in political science at the University Paris Nanterre and a member of the Institute for Social Sciences of Politics. Before her appointment at Nanterre, she was a Marie Curie fellow at the University of California, Berkeley. She is the author of Living by the Gun in Chad: Combatants, Impunity and State Formation (2016).